No, Melatonin is NOT For Sleep...
Jun 10, 2019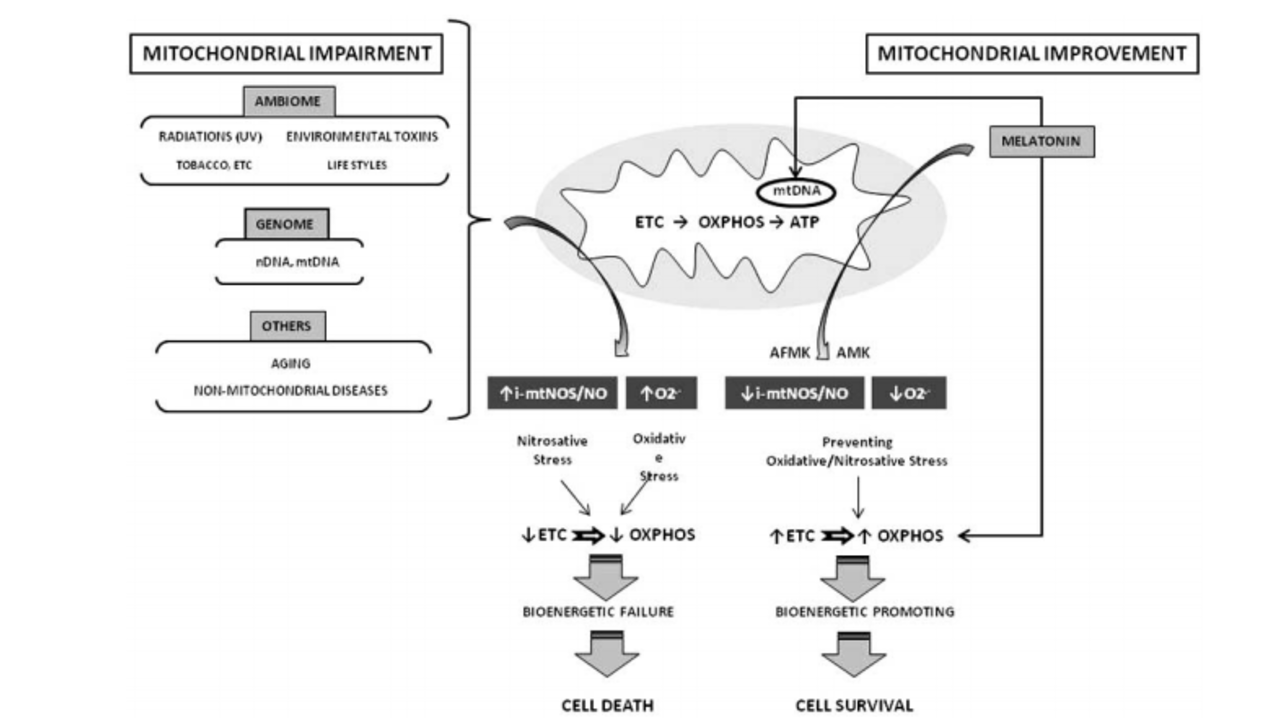
Ok, so I may have told a little half truth to get you to stop and read this quick but important post.
I should have said "Melatonin is not JUST for sleep".
Melatonin does have a something to do with your sleep but infinitely more important, melatonin is more of a SIGNAL of darkness that helps synchronize all your body clocks and repairs your mitochondria. Even though its a signal of darkness realize melatonin is built from aromatic amino acids like tryptophan that are synthesized in light! THIS is what you want to read this article for so don't go away.
Melatonin is really FOR your mitochondria.
A family member of mine never wears their blue light blocking glasses at night because they say, "I don't need to protect my melatonin, I can get to sleep just fine."
Well...this is an extremely dangerous practice to follow which you'll see plain as day below in a moment.
First a quick note on melatonin and sleep.
Melatonin is only half of the sleep equation.
The other important half is a chemical neurotransmitter called adenosine. Both melatonin and adenosine help you sleep through processes known as the circadian rhythm sleep wake cycle (melatonin) and the homeostatic sleep drive process (adenosine).
In the homeostatic sleep drive process, adenosine builds up and binds to adenosine receptors the longer you stay awake. The more adenosine you build up, the more tired you get. You build up large amounts of adenosine by being awake and breaking down the large amounts of ATP your mitochondria make. You can really understand how this works when you realize that the caffeine in coffee blocks adenosine from binding to adenosine receptors. Thats part of how coffee makes you less tired and more energized, it reduces the accumulation of adenosine.
In the circadian rhythm sleep wake cycle process, the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) takes light signals from your eye in the day time and suppresses the release of melatonin in areas of your body such as the pineal gland. As night approaches, photoreceptors in your skin and eyes known as melanopsin sense the dimming of the day light and the onset of dark and signal your SCN to start your body's release of melatonin which contributes to the nighttime sleepiness you feel.
So adenosine build up gets you sleepy first, then melatonin comes in to make you more sleepy and mainly improve the "quality" of your sleep. You can be a little low on melatonin and higher on adenosine and get to sleep just fine.
But that doesn't mean you are going to be........just fine....your sleep quality...the repair and regeneration you usually experience during sleep will be greatly reduced or impaired.
And it is no scientific secret that artificial light at night, especially light rich in the blue light wavelength from big tech like LEDs, Tvs and iphone screens will suppress your melatonin...big time.
Doctors and scientists have known this for years.
STUDY: Exposure to Room Light before Bedtime Suppresses Melatonin Onset and Shortens Melatonin Duration in Humans
The problem is that when you blunt the release or production of melatonin, your mitochondria suffer and break down faster over time which means you are the lucky one who gets a disease faster than you think you should (watch this Dr Doug Wallace lecture on Mitochondrial Heteroplasmy and mtDNA mutations).
Why do your mitochondria break down and become inefficient?
One of, if not the biggest reason, is because your mitochondria are repaired and optimized by melatonin! Autophagy, apoptosis, mitochondrial heteroplasmy. All of this is at least partially regulated by melatonin. Mitochondria are also loaded with melatonin receptors and actually synthesize their own melatonin as well.
Don't take my word for it, I'm only the simple minded author of The Blue Light Diet and creator of The Blue Light Detox program, I'm no brilliant doctor or biophysicist.
Why don't you take a look at the studies below from some of the best doctors, scientists and biophysicists in the world. Don't worry, as you'll see, none of these studies are from woo woo wacko websites. You can safely share each one to your Facebooks without fear of quackery accusations.
Just read the headlines now, dig into the research after you finish this article. It should lead to the largest health "Aha" moment you've ever had.
Melatonin Mitigates Mitochondrial Meltdown: Interactions with SIRT3
Mitochondria: Central Organelles for Melatonin′s Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Actions
Melatonin in Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Related Disorders
Melatonin protects lung mitochondria from aging
Melatonin: A Mitochondrial Targeting Molecule Involving Mitochondrial Protection and Dynamics
Melatonin, mitochondria, and the cancer cell
Melatonin-mitochondria interplay in health and disease.
Melatonin and mitochondrial dysfunction in the central nervous system.
Melatonin, a natural programmed cell death inducer in cancer.
Melatonin and human mitochondrial diseases
Mitochondrial functions and melatonin: a tour of the reproductive cancers.
Melatonin, cardiolipin and mitochondrial bioenergetics in health and disease.
Therapeutic potential of melatonin related to its role as an autophagy regulator: A review
Melatonin as an endogenous regulator of diseases: The role of autophagy
Melatonin and cell death: differential actions on apoptosis in normal and cancer cells
Melatonin as a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant: one of evolution's best ideas.
Synchronizing effects of melatonin on diurnal and circadian rhythms.
I can go on and on posting but I think you get the point.
The last thing you want if you care about your health is inefficient or bad mitochondria. Endogenous melatonin, meaning melatonin that your body makes on its own and not melatonin from a pill, optimizes your mitochondria.
So does that mean you shouldn't take melatonin supplements?
Well, taking melatonin supplements is very specific to the individual and can be ok in short term circumstances or maybe if the person has cancer or is older with severe melatonin deficiency or a heavy duty disease etc.
And as you age, your pineal gland calcifies and sometimes your melatonin receptors lose their sensitivity. Melatonin supplementation may be ok in this case.
You must BLOCK THE BLUE LIGHT and lower the lux while taking melatonin supplements though. It is a hormone of darkness.
But for most of us, taking melatonin supplements chronically probably isn't such a good idea.
First of all, when you take a melatonin pill, many times it remains in your system at high concentrations the next day! Sometimes people even feel a "melatonin hangover" because of this. This is not good for your circadian rhythm. Melatonin levels are supposed to crash during the day.
Plus there is evidence that taking melatonin supplements at night without blocking blue light thins your retina and damages how your eye works, especially causing photoreceptor damage.
When you change the shape of your eye, your eye can't process light correctly. When you destroy photoreceptors, your body can't use light. All of this means that disease will probably visit you faster.
Realize right now, you are learning cutting edge information that hasn't trickled down to your family doctor or general practitioner yet. They haven't had time to read any of this (HINT: forward them this article).
So this is a melatonin-mitochondrial matrix movie moment for you.
There are two pills you can take.
The red or the blue.
Take the blue pill and you can go back to your ordinary life. Eating well, exercising and seeing your general practitioner for your yearly physical and pretending that is enough to stay healthy and live long without any surprise diseases that seemingly pop up out of nowhere one day.
Or....
You can take the red pill starting today.
Realize that it is not just diet and exercise and getting a yearly physical that keeps you healthy.
Light is arguably, and in my opinion, more important than diet and exercise for health and it is about damn time you start paying attention to it.
If you get artificial light at night, you are destroying your melatonin which means you are destroying your mitochondria!
How's that for an "Aha" health moment?
So how do you start paying attention to light and protecting/producing more melatonin in order to repair and slow the decline of your mitochondria?
Make sure to complete the endogenous melatonin mitochondrial loop every day.
1) See the sunrise every morning. The specific frequencies of light (blue, red and a little bit of purple (uv) ) and their interaction with the amino acid tryptophan at and around sunrise shut down the release of melatonin and start the production and regeneration of melatonin in your eye. From there the melatonin cascade begins, melatonin is synthesized in multiple cells and areas of your body throughout the rest of the day and night, the most circulating melatonin coming from the pineal gland.
2) See the sunset and BLOCK blue and green light wavelengths after sunset from hitting your eyes. At sunset, the color temperature of light increases greatly and then drops quickly. Melanopsin photoreceptors in your eye detect the dimming of the light and start the process of melatonin release. The blue and green wavelengths of light have been found to destroy these photoreceptors, trigger intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells in your retina to tell your SCN it is basically daytime and suppress melatonin. Because of this, you need to wear special blue and green light blocking glasses at night. You may as well cover up your skin after sunset as well since we now know their are melanopsin photoreceptors in your skin and fat.
Even if you wear the blue green light blocking glasses, it is a good idea to keep the lights down low at night anyway because the brighter they are, the more they suppress melatonin. A "LUX" measurement can be used to measure the brightness of light in your home at night. Everyone's circadian system varies in how sensitive it is to artificial light at night, but as you'll discover in this study, on average, you see at least a FIFTY PERCENT suppression of melatonin with just 30 lux of light at night.
Get a cheap lux meter on Amazon and make sure your lights measure under 30 LUX at night.
That simple melatonin mitochondrial loop, seeing the sunrise/getting morning sun and seeing the sunset/blocking blue/green light at night encodes the basic steps for melatonin and mitochondrial optimization.
What are my favorite blue light blocking glasses?
It kind of depends on where you are located in the world but here are a few I know work because I have tested them.
1) EMR Cyclops - Use the code "bluelight" for a discount.
2) RA Optics - Use the code "bluelightdiet10" for a discount.
3) BluBLOX - Use the code "bluelightdiet" for a discount.
4) TrueDark - Use the code "bluelightdiet" for a discount.
If you would like to go deeper, make sure to read The Blue Light Diet or enroll in the Blue Light Detox Program where I will personally walk you through everything, step by dimly lit step.
If you are like my blabbering "I don't need to wear no blue blockers at night" family member, take our free blue light toxicity test here and find out if you do.
If you found this article valuable, please help me out by sharing it on your Facebooks or social media pages. And show it to your doctor!!
On to the next one....
WANT TO LEARN MORE ABOUT LIGHT & HEALTH?
Sign up below now to get the free Blue Light Diet cheat sheet to light and health.
We hate SPAM. We will never sell your information, for any reason.

